Introduction
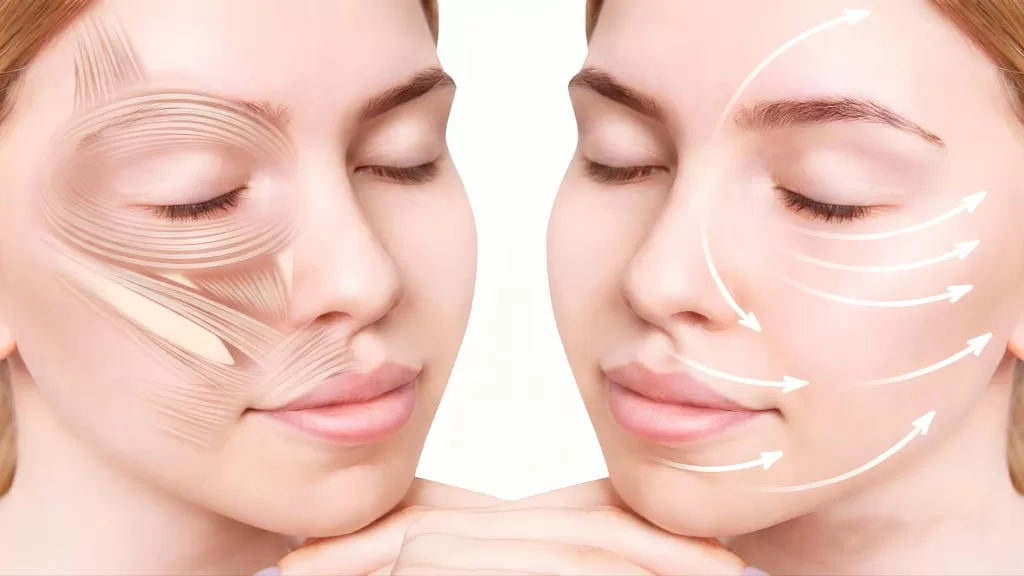
The SMAS Facelift is widely regarded as the gold standard for correcting deeper signs of facial aging, because it targets the Superficial Musculoaponeurotic System—the structural layer responsible for facial support, contour, and firmness. Traditionally performed through surgery, the SMAS Facelift has delivered dramatic and long-lasting lifting results for decades. But with growing demand for safer, non-invasive rejuvenation, many patients today are asking whether they truly need surgery. According to clinical research published by the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI), non-surgical skin tightening technologies—particularly ultrasound HIFU-based devices—have become a cornerstone of the global anti-aging field.
This article explains the difference between HIFU and SMAS Facelift, the science behind both approaches, and why modern technologies like PZLASER’s MFUPRO™ represent the next generation of precise, medical-grade SMAS rejuvenation.

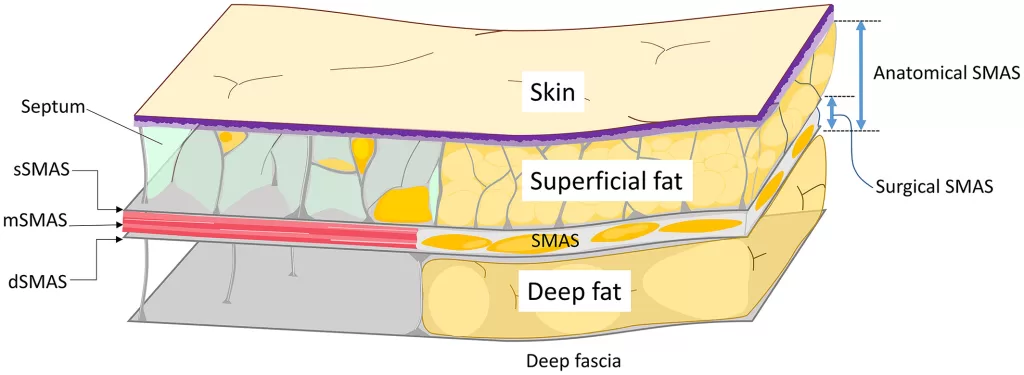
What Is the SMAS Layer?
The Superficial Musculoaponeurotic System (SMAS) is a strong, fibromuscular layer located between the subcutaneous fat and the deeper facial muscles. It acts as a support framework that shapes the cheeks, jawline, and midface.
Key Characteristics of the SMAS
- Connects facial muscles with the dermis
- Provides structural lifting and support
- Determines the tightness and contour of the face
- Loosens naturally with aging, gravity, and collagen loss
When the SMAS layer weakens, the visible results include:
- Sagging cheeks
- Nasolabial folds
- Jowls
- Drooping jawline
- Neck laxity
This is why effective lifting must target the SMAS, not just the superficial skin.
Why Is the SMAS Layer Important for Facial Lifting?
Aging affects all layers of the face, but the SMAS is the most critical because:
- It is responsible for structural support
- It holds the fat pads and muscles in their youthful positions
- Its laxity causes most visible signs of aging
Traditional surgical facelifts focus on repositioning the SMAS rather than only tightening the superficial skin. Similarly, modern non-invasive technologies must reach the SMAS to create significant lifting.
Common Methods for SMAS Facelift
1. Surgical SMAS Facelift
The surgical facelift (rhytidectomy) is the original and most definitive method of addressing SMAS laxity.
History
- First developed in the mid-20th century
- Evolved to include SMAS repositioning and deep-plane techniques
- Still considered the gold standard for dramatic lifting
Advantages
- Long-lasting results (8–12 years)
- Significant lifting and repositioning
- Effective for severe sagging
Limitations
- Invasive
- Requires anesthesia
- Weeks of downtime
- Higher cost
- Potential surgical risks (nerve injury, scarring, asymmetry)
2. Thread Lifting
Thread lifting uses barbed or cone-based sutures to reposition the SMAS indirectly.
Pros
- Minimally invasive
- Immediate results
Cons
- Shorter results
- Risk of thread visibility
- Not suitable for all face types
3. RF (Radiofrequency) Lifting
Used widely for tightening dermal layers, but cannot reliably reach the SMAS layer
Pros
- Improves skin texture and fine lines
Cons
- Does not create true SMAS lifting
- Mostly superficial tightening
4. HIFU (High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound)
The first non-invasive technology capable of reaching the SMAS layer.
This is where the story changes.
HIFU: Evolution of Non-Invasive SMAS Lifting
- Originally developed for medical applications (tumor ablation)
- Introduced into aesthetics in the early 2000s
- Commercialized globally with medical devices like Ultherapy
How HIFU Works?
HIFU delivers focused ultrasound energy deep into the tissue to create thermal coagulation points at precise depths:
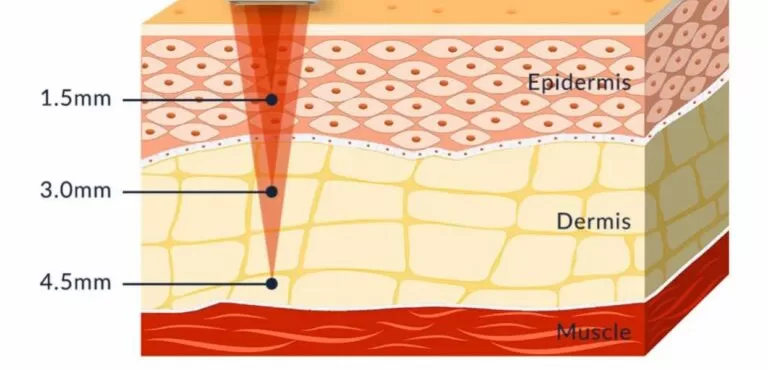
- 1.5 mm – superficial dermis
- 3.0 mm – deep dermis
- 4.5 mm – SMAS layer
Some advanced devices support 6–9 mm for subcutaneous tightening.
The thermal effect leads to:
- Immediate collagen contraction
- Long-term neocollagenesis
- Gradual lifting over 60–90 days
Advantages of HIFU
- 100% non-invasive
- No downtime
- Precise targeting
- Natural collagen remodeling
Limitations of HIFU
Not all HIFU devices are equal. Limitations include:
- Inconsistent energy output in low-quality devices
- Discomfort during treatment
- Variable results based on cartridge quality
- Narrow treatment coverage in traditional HIFU lines (point-line matrices)
Main Difference Between HIFU and SMAS Facelift
| Category | HIFU (Technology) | SMAS Lifting (Outcome) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Non-invasive ultrasound energy | Tightening/repositioning of SMAS layer |
| Nature | A method | A result |
| Target Depth | 1.5–4.5 mm (depending on device) | SMAS (4.5 mm+), deep layers |
| Invasiveness | Non-invasive | Can be surgical or non-surgical |
| Result | Collagen remodeling and tightening | Structural lifting |
| Recovery | No downtime | Depends on method |
| Tools | Devices like MFUPRO™, Ultherapy | Surgery, threads, HIFU |
| Suitability | Mild to moderate laxity | Moderate to severe laxity |
HIFU is a technology that can achieve SMAS Facelift, but not all HIFU devices have precise SMAS-targeting capability. Quality matters.
MFUPRO™: The Next-Generation SMAS Facelift System by PZLASER
PZLASER, with 20+ years of R&D experience and global certification achievements, has developed MFUPRO™, an advanced multi-functional focused ultrasound platform engineered for accurate, safe, and clinically effective SMAS facelift.

What Makes MFUPRO™ Unique?
MFUPRO™ is designed to solve the limitations of traditional HIFU:
- Unstable energy
- Low patient comfort
- Limited treatment precision
- Poor coverage
Core Advantages of MFUPRO™
1. Multi-Layer Ultrasound Rejuvenation
10D MFUPRO™ covers epidermis → dermis → subcutaneous tissue → SMAS → muscle layers, thanks to:
- 6 adjustable treatment depths
- 10 professional cartridges
- Medical-grade energy stability
2. More Precise, More Scientific
Advanced ultrasound focusing ensures:
- High penetration accuracy
- Uniform thermal nodes
- True SMAS contraction
- Reduced pain with controlled pulses
3. Intelligent Performance System
MFUPRO™ integrates:
- Smart energy tracking
- Temperature monitoring
- Optimized pulse stability
- Uniform output for consistent lifting
4. Broader Indications
MFUPRO™ effectively treats:
- Facial sagging
- Double chin
- Jawline laxity
- Neck wrinkles
- Brow ptosis
- Textural roughness
- Dermal tightening
5. Professional Clinical-Level Results
Compared to conventional HIFU, MFUPRO™ delivers:
- Deeper contraction
- Better safety
- Wider treatment area
- Faster regeneration
Conclusion
SMAS represents the core structural layer responsible for facial firmness and contour. While traditional surgical procedures historically dominated the SMAS lifting domain, modern technologies like HIFU have made non-invasive SMAS lifting widely accessible.
However, not all ultrasound devices are equal. MFUPRO™ stands out as a new generation of professional SMAS lifting technology, playing a crucial role in delivering natural, long-lasting facial rejuvenation—beyond superficial tightening, and into true structural SMAS remodeling.